difference between cables and wires
by:AAA
2021-03-05
The wire is composed of one or several soft wires, and the outer covering is light and soft; the cable is composed of one or several insulated coated wires, and the outside is covered with a tough outer layer made of metal or rubber. Cables and wires generally consist of three parts: core wire, insulating sheath and protective sheath. The characteristics of commonly used cables are as follows: CEF-ethylene propylene rubber insulated neoprene sheath, flame-retardant power cable for ships. CVV-PVC insulated, PVC sheathed flame-retardant power cable for ships. Oxygen chamber wires often use BV, BX, RV, RVV series wires, among which: BV――copper core PVC insulated wire, long-term allowable temperature 65℃, minimum temperature -15℃, working voltage AC 500V, DC 1000V, fixed laying It can be applied both in the open and in the dark. BX――Copper core rubber insulated wire, with a maximum operating temperature of 65°C, for laying indoors. RV――Polyvinyl chloride insulated single-core flexible cord, maximum operating temperature 65℃, minimum operating temperature -15℃, working voltage AC 250V, DC 500V, used as internal wiring of instruments and equipment. RVV-copper core PVC insulated and sheathed flexible wire, allow long-term working temperature 105 ℃, working voltage AC 500V, DC 1000V, used in humid, high mechanical protection requirements, frequent movement and bending occasions. In fact, there is no strict boundary between 'wire' and 'cable'. Generally, products with a small number of cores, small product diameters, and simple structures are called wires, those without insulation are called bare wires, and the others are called cables; those with a larger conductor cross-sectional area (greater than 6 square millimeters) are called large wires. Small (less than or equal to 6 square millimeters) are called small wires, and insulated wires are also called cloth wires. This is relatively simple and easy to understand!! Cables generally have more than two layers of insulation, most of which are multi-core structures and are wound around the cable reel. Above, the length is generally greater than 100 meters. Wires are generally single-layer insulated, single-core, 100-meter rolls, wireless disks. Common cable types: VV means: PVC insulation (first V), PVC sheath (second V) YJV22 means: cross-linked polyethylene insulation (YJ), PVC sheath (V), Steel tape Kaizhuang (22) The model number with 'ZR' or 'FR' is flame-retardant cable (wire). The type of aluminum wire with 'L' is simpler: BVV--PVC insulated and sheathed copper core wire, BV--PVC insulated copper core wire, BYJ--copper core cross-linked polyolefin insulated wire, BVR--PVC insulated copper core cord, BX--rubber insulated copper core cord, RHF--chloroprene rubber sheathed copper core cord.
(2) The smaller diameter is called 'line'; the larger diameter is called 'cable'.
(3) The simple structure is called 'line'; the complicated structure is called 'cable'.
But with the expansion of the scope of use, many varieties 'cable in the cable' and 'cable in the cable'. So there is no need to make a strict distinction.
In daily habits, people call household cloth wires a wire, and power cables abbreviate to cables.
Under normal circumstances, we refer to wires and cables as wires and cables. There is no precise and fixed conceptual distinction between wires and cables, and the distinction is generally only made based on daily experience. In a narrow sense, it is divided into wires and cables, and in a broad sense, they are generally collectively referred to as cables. So, what is the difference between wire and cable?
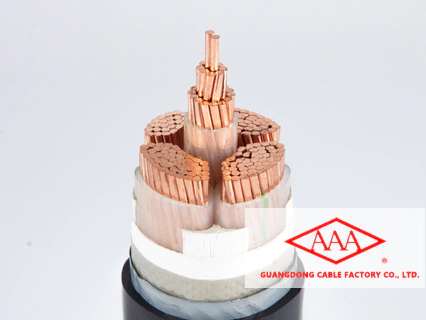
Wires and cables are generally composed of three parts: wire and cable conductor, insulation layer and sheath layer. Wire generally refers to a type of wire and cable that is formed by twisting a single or multiple conductors such as copper or aluminum, and then adding an insulating layer or sheath layer to the outside of the wire and cable conductor. A cable is generally composed of one or more conductors, and each conductor of the cable is formed by twisting one or more conductors, and then covered by insulation or sheath. To put it simply, each conductor of the cable A conductor can be counted as a strand of wire. This is the most straightforward difference between wire and cable.
According to the physical shape of the conductor, wires can be divided into solid conductors, stranded conductors, braided conductors and other types. According to whether the wires and cables have an insulating layer, they can be divided into bare wires and insulated wires. Bare wires refer to wires with no insulation layer or protective sheath outside the wire conductor. The cable can be understood as a large wire with a conductor core composed of one or more independent insulated wires and a protective layer. The number of conductor cores of a wire is generally small. At the same time, the diameter of the wire conductor is relatively small and the structure is relatively simple. The cable has a large number of conductor cores, a larger diameter, and a more complex structure. For example, some cables have steel tapes, some cables have braids, and so on.
Wires are generally used for daily household use, such as threading, lead wires, etc., and also used for home appliance manufacturing, motor component connection, power supply facility connection, etc., to transmit low-power electrical energy and signal lights. Cables are generally used to transmit, distribute, and transmit strong electrical energy or signals in the power supply line, and they pass large currents (tens of amperes to several thousand amperes) and high voltages (220V to 35kV and above). Cables are generally divided into power cables, shielded cables, control cables, etc. according to their uses.
To sum up, in general, we define wires and cables as wires with a single conductor and cables with multiple conductors. A conductor with a smaller diameter is called a wire, and a conductor with a larger diameter is called a cable. Wires and cables with simple structures are called wires, and those with complex structures are called cables.
Simply put, wires only have an insulation layer, while cables have a sheath layer besides the insulation layer.
A single wire is generally used, which can be combined at will. For example, for ordinary lights, we use two single wires and sockets, and we use three single wires, so it is generally better to calculate the length of a single wire.
Because the cable has a sheath layer, relatively speaking, the number of cables cannot be combined at will. If there are 5 cables, there are 5 insulated wires in the sheath, which are all finished products, so the length is directly calculated.
NHVV is a cable, it does not need to be multiplied by 5. NH means fire resistance.
A wire is composed of one or several soft wires with a light and soft sheath; a cable is composed of one or several insulated coated wires, and the outside is covered with a tough outer layer made of metal or rubber.
Cables and wires are generally composed of three components: core wire, insulating sheath and protective sheath.
Custom message